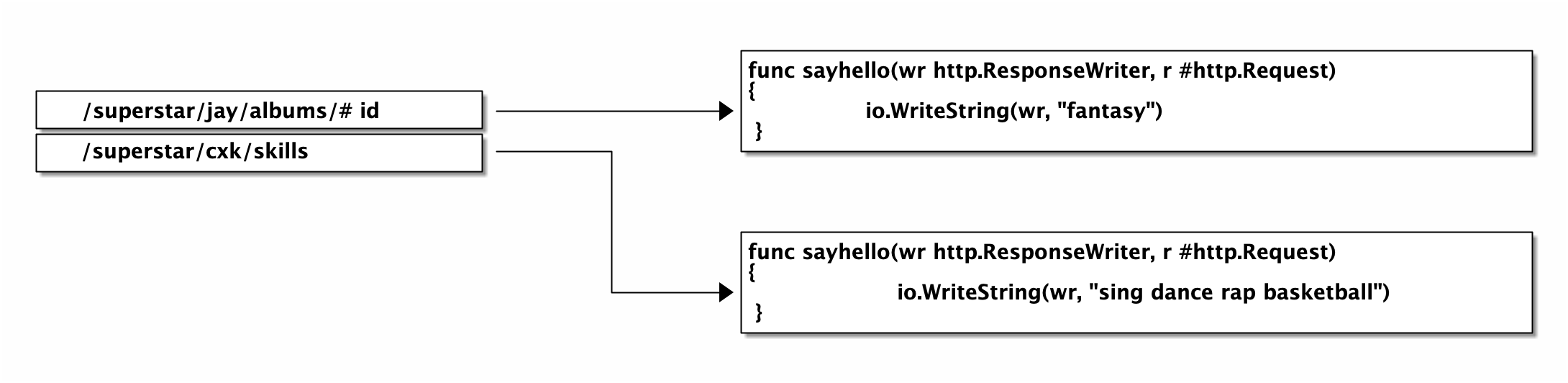
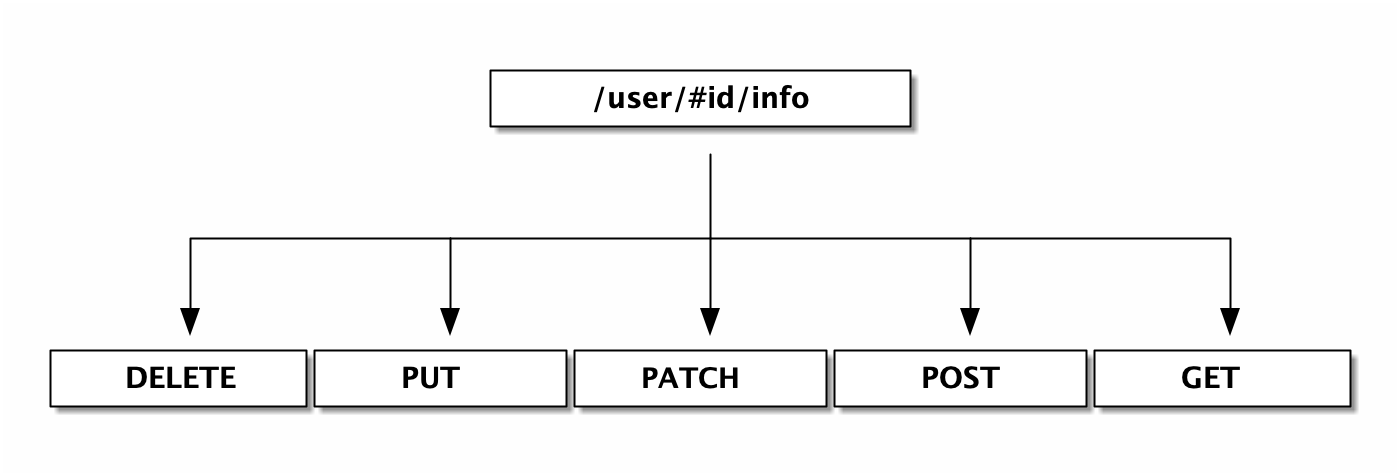
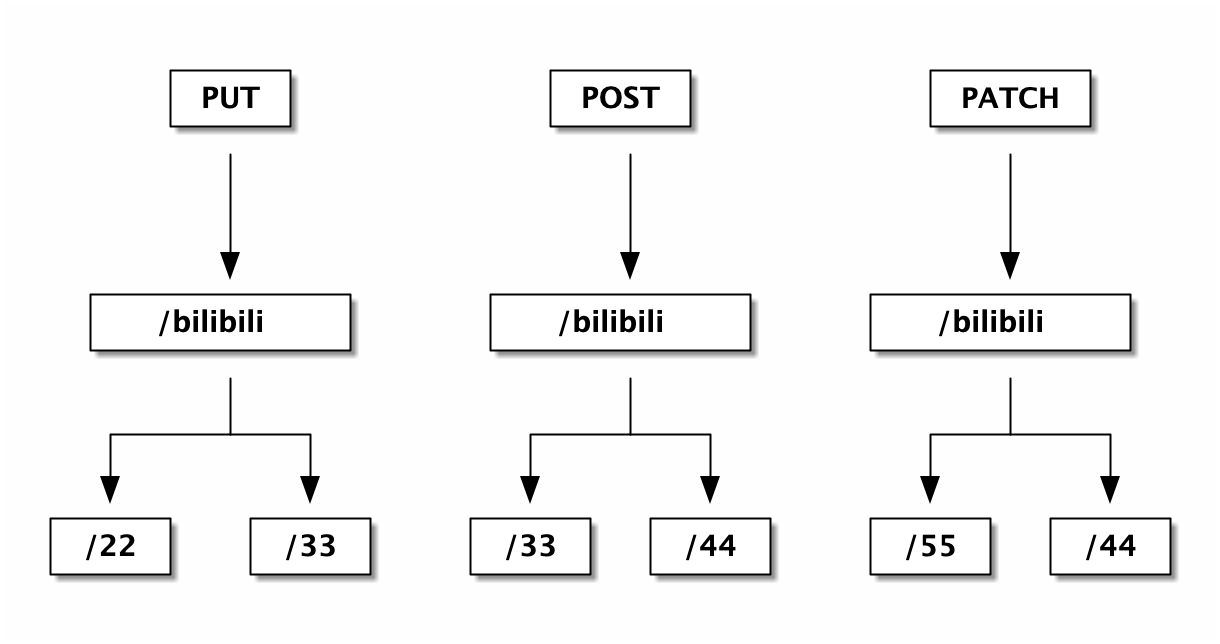
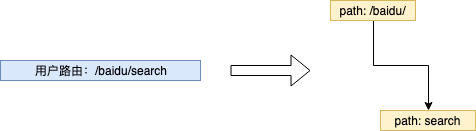
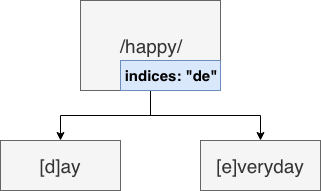
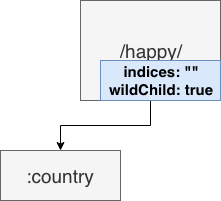
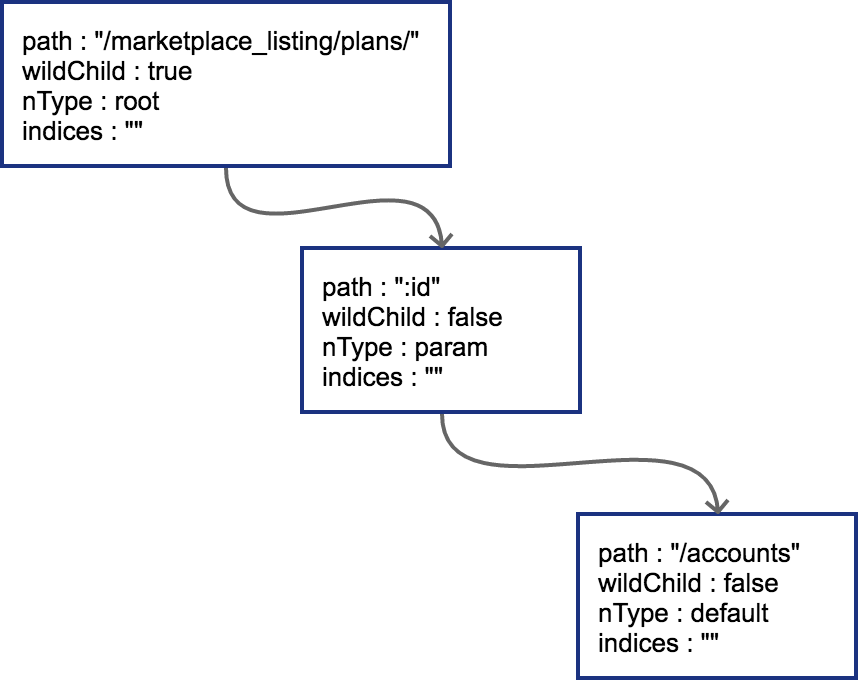
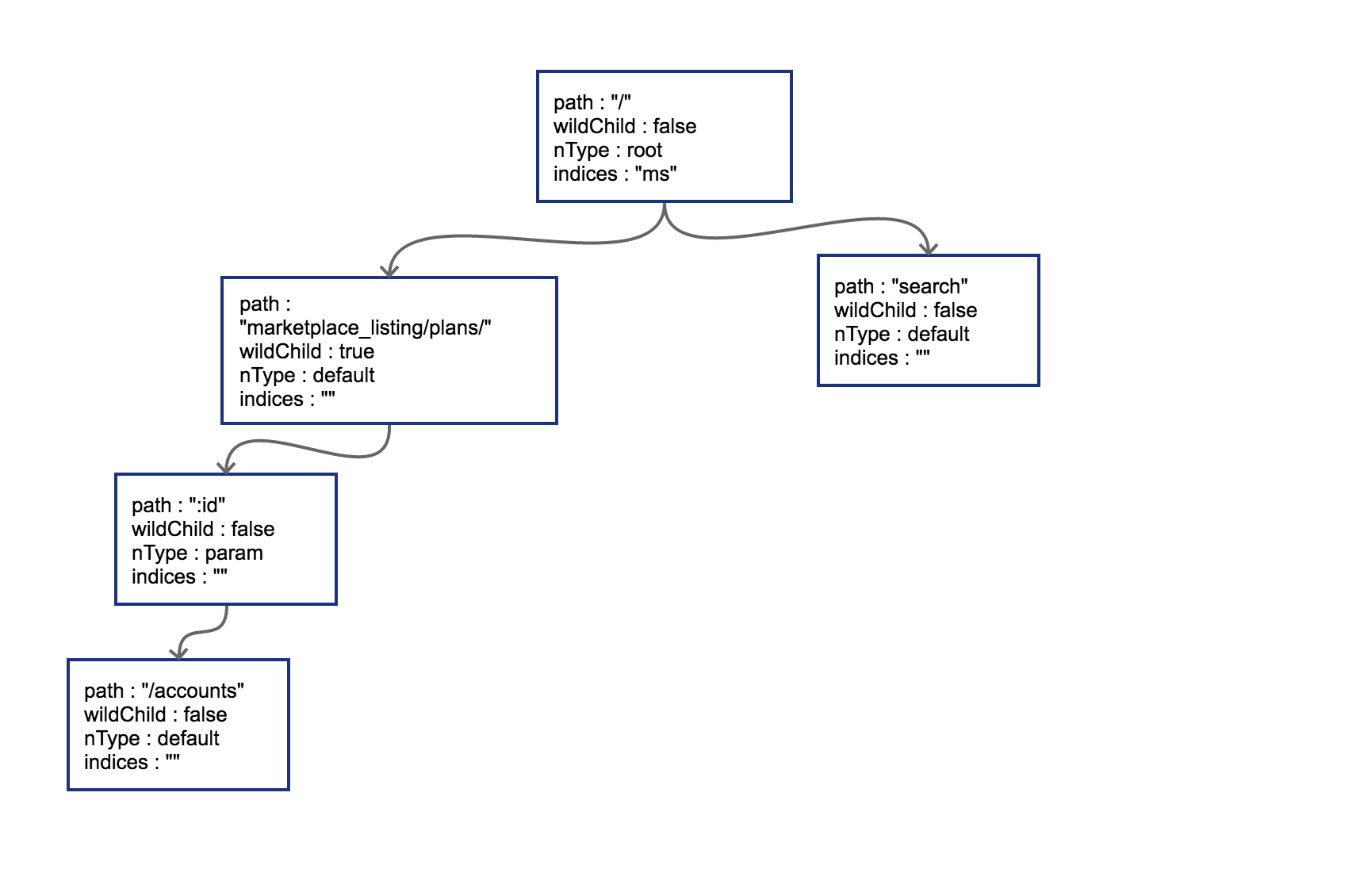
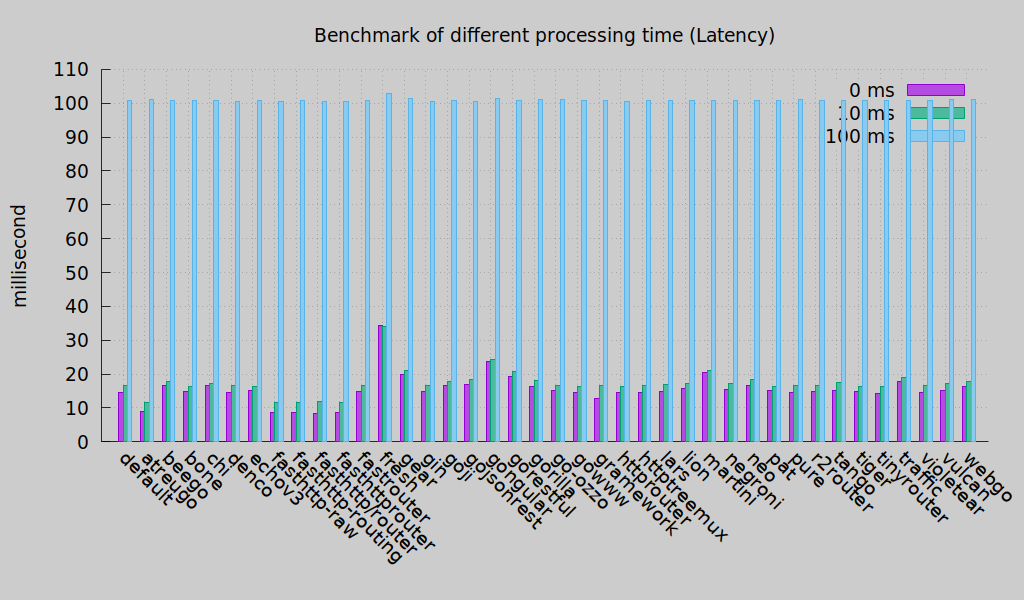
http router 构造
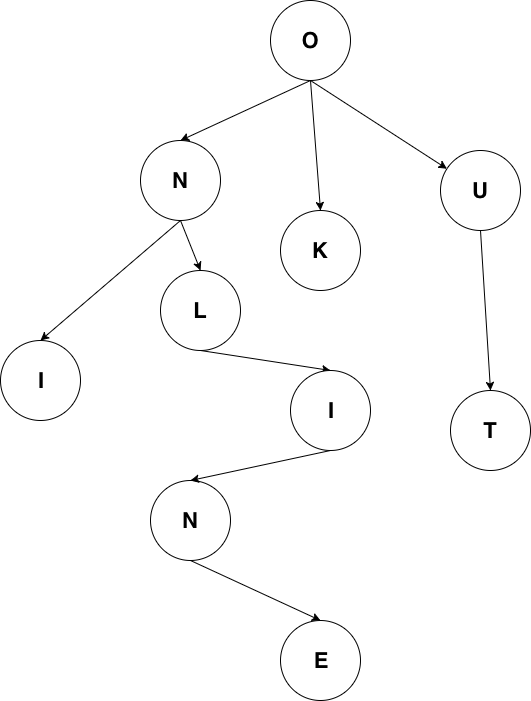
普通的 trie
-
单个节点代表一个字母
-
如果需要对字符串进行匹配
-
只要从根节点开始依次匹配即可
普通的 trie 有什么缺点呢?
在主要的英文字典中,最长的单词是 pneumonoultramicroscopicsilicovolcanoconiosis,由45个字母组成,意思是一种肺部疾病(由于吸入超显微硅酸盐及石英尘所引起的)肺尘埃沉着病”,通称火山矽肺病。其中,pneumo-表示“肺”,ultra-表示“超”,microscopic意为“微观”,silico-表示“硅”,volcano指“火山”,coni-意思是“尘”,-osis为表示疾病的后缀。后来研究者认为这是一个大骗局。
最长的英文单词
-
树的深度和路由字符串长度正相关
-
占用较多的内存
-
字符串越长,匹配越慢(类似链表结构,在内存中存储不连续的数据)
radix tree
In computer science, a radix tree (also radix trie or compact prefix tree) is a data structure that represents a space-optimized trie (prefix tree) in which each node that is the only child is merged with its parent. The result is that the number of children of every internal node is at most the radix r of the radix tree, where r is a positive integer and a power x of 2, having x ≥ 1. Unlike regular tries, edges can be labeled with sequences of elements as well as single elements. This makes radix trees much more efficient for small sets (especially if the strings are long) and for sets of strings that share long prefixes.
在 http 路由的场景下 一棵 radix tree 是不够用的 为什么呢?
httprouter 中的一些概念
路由冲突
路由发生冲突,主要是 static 节点、param 节点、catchAll 节点之间冲突,例如:
一个例子
conflict:
GET /user/info/:name
GET /user/:id为什么会冲突呢?因为 param 节点和普通字符串节点是没有办法共存的。例如输入路由字符串为:/user/info,在 /user/:id 规则中,info 会被解释为 :id 的值。
no conflict:
GET /user/info/:name
POST /user/:id两个路由的 HTTP Method(GET/POST) 不同,因此会在不同的 radix tree 上。
所有情况
-
在插入 wildcard 节点时,父节点的 children 数组非空且 wildChild 被设置为 false。例如:GET /user/getAll 和 GET /user/:id/getAddr,或者 GET /user/*aaa和 GET /user/:id。
-
在插入 wildcard 节点时,父节点的 children 数组非空且 wildChild 被设置为 true,但该父节点的 wildcard 子节点要插入的 wildcard 名字不一样。例如: GET /user/:id/info 和 GET /user/:name/info。
-
在插入 catchAll 节点时,父节点的 children 非空。例如: GET /src/abc 和 GET /src/*filename,或者 GET /src/:id 和 GET /src/*filename。
-
在插入 static 节点时,父节点的 wildChild 字段被设置为 true。
-
在插入 static 节点时,父节点的 children 非空,且子节点 nType 为 catchAll。
很好理解,能看懂下面这张图就行:
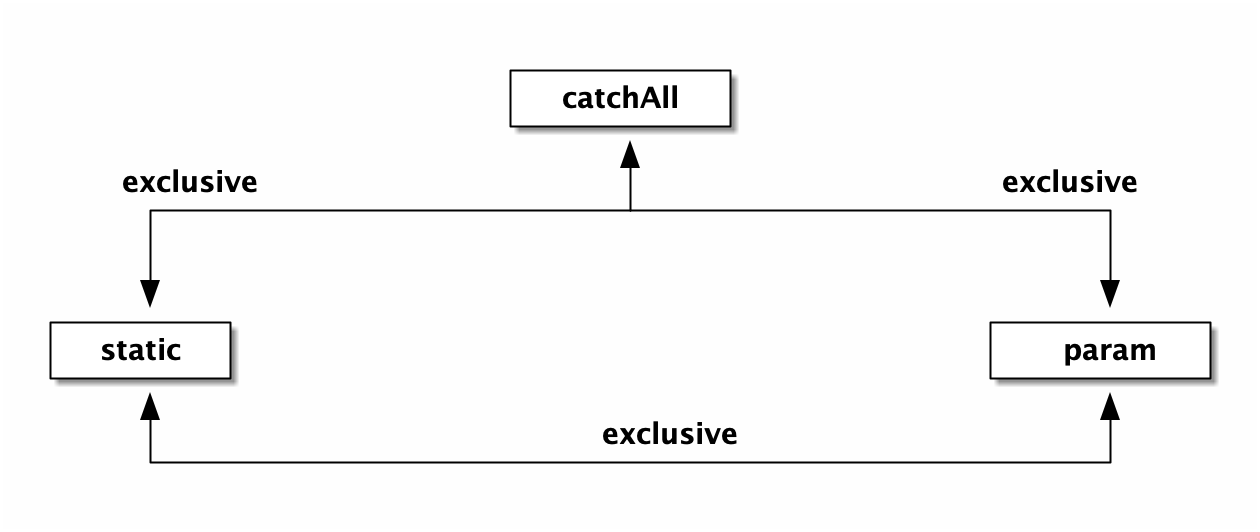
即同一个节点,其子节点的情况只可能是:
-
一个 wildcard 节点
-
一个 catchAll 节点
-
一个或多个 static 节点
路由功能扩展
上面我们看到,httprouter 中只有 static/param/checkAll 这三种节点。有一部分人认为功能不够强大。
我们可以思考如何对标准的 httprouter 功能进行扩展。
目前 param 节点和 static 节点无法共存,如果我们想让 param 和 static 可以共存的话呢?
-
/cars/{id : \d+}
-
/cars/f1
上面这两条路由显然是可以共存的,我们可以先匹配 /cars/f1,不匹配的情况下再去尝试匹配 /cars/{id: \d+},都不匹配,则 404。
想实现这个功能也不难,可以自行尝试。
拓展阅读:RESTFul 和 GraphQL 之争
看看就行了。该 post 一把梭的时候连 RESTFul 都不用,更不用说 GraphQL 了。
对于有些公司的人来说,RESTFul 都接不利索(比如 Go 标准库中的 http client,用 PUT/PATCH 之类的方法就很不方便,开源的 http client 各种 bug)。
Go 夜读调查问卷

Please do not obsess over routers. Their difference in speed, if any, is negligible compared to the network and disk IO of a standard web app. Just pick one and move on.
分享过程中有同学问的没有回答的两个问题:
|
httprouter 是不是不支持 /:hashcode 这种路由? |
是支持的,必须以 / 开头才行
|
这些路由的 zero garbage 和 0 alloc 是咋实现的? |
zero garbage 指进程不在堆上分配内存。http router 实现了全静态路由时,匹配过程 0 alloc,这里的 0 次分配其实就是没有堆内存分配(栈上的肯定还是有的,但栈上分配内存不影响 GC)。
但 httprouter 在路由中含有参数时,会额外分配一个 Params 的 slice,提供给用户的 handler 来使用。所以可以看到,带参数的路由在 httprouter 的 benchmark 中有 alloc:
BenchmarkHttpRouter_Param 20000000 139 ns/op 33 B/op 1 allocs/op下面是 gin 的 benchmark:
BenchmarkGin_Param 20000000 113 ns/op 0 B/op 0 allocs/opGin 用的也是 httprouter,但是为什么这里却是 0 alloc 呢?答案很弱智,sync.Pool:
// Engine is the framework's instance, it contains the muxer, middleware and configuration settings.
// Create an instance of Engine, by using New() or Default()
type Engine struct {
RouterGroup
// ....
pool sync.Pool
// ....
}感兴趣的同学可以自己追一下代码。